Harmonic Distortion Analyzer
A Harmonic Distortion Analyzer measures the total harmonic power present in the test wave rather than the distortion caused by each component. The simplest method is to suppress the fundamental frequency by means of a high pass filter whose cut-off frequency is a little above the fundamental frequency. This high pass allows only the harmonics to pass and the total harmonic distortion can then be measured. Other types of Harmonic Distortion Analyzer based on fundamental suppression are as follows.
Another application is the measurement of the effectiveness of an electronic filter with an extremely narrow passband, such as a notch filter in a parametric equalizer.
1. Employing a Resonance Bridge:
The bridge shown in Fig. 9.5 is balanced for the fundamental frequency, i.e. L and C are tuned to the fundamental frequency. The bridge is unbalanced for the harmonics, i.e. only harmonic power will be available at the output terminal and can be measured. If the fundamental frequency is changed, the bridge must be balanced again. If L and C are fixed components, then this method is suitable only when the test wave has a fixed frequency. Indicators can be thermocouples or square law VTVMs. This indicates the RMS value of all harmonics. When a continuous adjustment of the fundamental frequency is desired, a Wien bridge arrangement is used as shown in Fig. 9.6.
The bridge is balanced for the fundamental frequency. The fundamental energy is dissipated in the bridge circuit elements. Only the harmonic components reach the output terminals. The harmonic distortion output can then be measured with a meter. For balance at the fundamental frequency, C1 = C2 = C, R1 = R2 = R, R3 = 2R4.
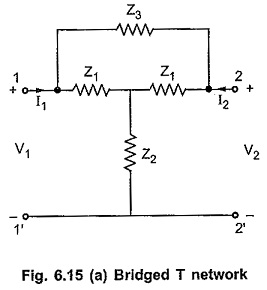
3. Bridged T-Network Method:
Referring to Fig. 9.7 the, L and C’s are tuned to the fundamental frequency, and R is adjusted to bypass fundamental frequency. The tank circuit is tuned to the fundamental frequency, the fundamental energy will circulate in the tank and is bypassed by the resistance. Only harmonic components will reach the output terminals and the distorted output can be measured by the meter. The Q of the resonant circuit must be at least 3-5.One way of using a bridge T-network is given in Fig. 9.8.
The switch S is first connected to point A so that the attenuator is excluded and the bridge T-network is adjusted for full suppression of the fundamental frequency, i.e. minimum output. The minimum output indicates that the bridged T-network is tuned to the fundamental frequency and that the fundamental frequency is fully suppressed.
Advantages of Harmonics Analyser
Harmonic currents that are generated by industrial as well as electrical equipment in offices usually reflect in the surging electricity bills. Here, a harmonics analyzer comes to your rescue. It helps in quantifying the costs and also saves a lot of energy. This is particularly beneficial in the industry sector where the power consumption is maximum. Let’s take a look at the advantages of a harmonics analyzer:
- A harmonic analyzer is a device that is used to measure frequencies, amplitudes, different phases, and various components of a non-sinusoidal waveform. It mainly consists of multipliers, an input device, and integrators.
- The harmonic analyzer is used to check harmonics in electrical systems. Harmonics are electrical voltages and currents that can result in power problems in the electrical system. The high harmonic voltage causes failure in machinery and equipment. Harmonic distortion is a concern among various industrial sectors in India. The impact of the harmonic distortion depends on how much the electrical power system can withstand and the susceptibility of the equipment to harmonic voltage.
- The harmonic analyzer is the best equipment to carry out a detailed power quality analysis in the facility in order to determine the wave shapes of the current and voltage on their frequency spectrums.
- Harmonic analyzers are helpful in providing a thorough analysis of the suspected source of harmonic voltage. This data is used to calculate the harmonic ratio function at a value that ranges from 0% to 100%. This indicates the deviation of both the sinusoidal and sinusoidal waveforms. The resulting values indicate the presence of harmonic voltage. Electricians use a harmonic analyzer to detect harmonic voltage, thereby preventing any further damage to the equipment and saving repair costs.
- Using a harmonic analyzer, industries can significantly improve their energy efficiency by adopting all possible measures. With the early detection of harmonic voltage, industries can replace their older equipment, reducing the risk of any further damage or complete shutdown of the equipment.








No comments